By Paul Ejime

(Paul Ejime is a Global Affairs Analyst and Consultant on Peace & Security and Governance Communications)
After weeks of condescending defiance, France has ultimately eaten a diplomatic humble pie served by a former colony. Paris’ Ambassador to Niger was whisked away from Niamey in the wee hours of Thursday 27 September, two months after President Mohamed Bazoum, a French ally was toppled in a military coup led by Brig.-Gen Abdourahamane Tchiani on 26 July 2023.
The junta had on 28 August ordered Ambassador Silvain Itte to leave Niger within 48 hours, accusing him of refusing to honour an invitation to the Foreign Ministry. His action was in line with the French stand of withholding recognition to the military regime.
French President Emmanuel Macron had insisted that deposed and detained Bazoum was the elected and only legitimate authority in Niger, describing the military regime as illegal.
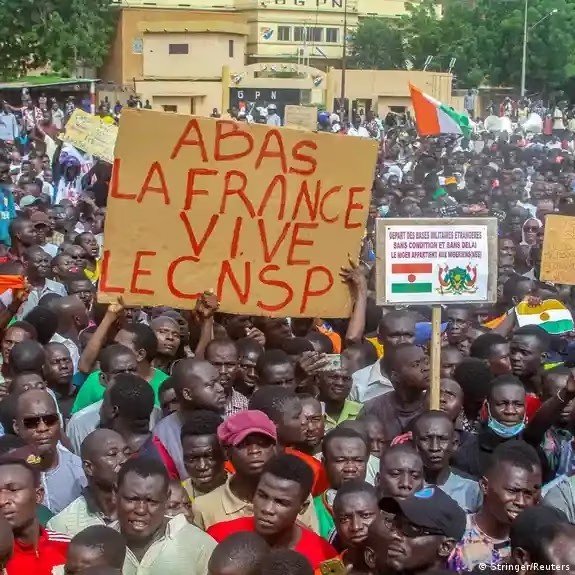
Following the expiry of the 48-hour ultimatum, the Tchiani-led junta, having effectively severed most contacts with France, with a demand for the withdrawal of some 1,500 French troops from Niger, announced that the Ambassador had been stripped of all diplomatic immunity.
Police were subsequently ordered to kick out the French envoy, while Niger citizens staged daily protests at the entrance of the French embassy and military bases in Niamey.
Amid the stand-off and heightened tension, with the envoy helmed in and virtually living on military rations, President Macron announced on Sunday that Ambassador Itte would leave Niger within hours, to be followed by the withdrawal of French troops by year end.
Diplomatic sources have confirmed Ambassador Itte’s arrival in France on a flight via Niger’s neighbouring Chad.
While his deputy is believed to still be in Niger for possible rapprochement in the future, analysts consider this incident as another major diplomatic blow to France in a growing number of its former African colonies given that the military regimes in Mali and Burkina Faso have taken similar anti-French measures.
With two other Francophone countries of Guinea and Gabon also under military dictatorships, the band of African leaders formerly sympathetic to the French cause is shrinking rapidly, yielding place to a groundswell of anti-French sentiments among the citizens.
There could be consequences from eventual withdrawal of French troops from the security-challenged West Africa and the Sahel region, even with the mutual defence pact announced recently by Mali, Guinea and Burkina Faso. But President Macron has not helped matters either, with his imperialist posture and grandstanding.

He is on record as saying that “without France, countries like Mali, Burkina Faso…. would not exist.” Such inflammatory statements are unhelpful when juxtaposed with the lopsided relations between France and its former African colonies, characterised by controversial post-independent agreements which gave Paris overbearing political and economic influence and control over the fortunes of these countries.
Under the patronising agreements, France has set up military bases in most of the countries with guaranteed right of first refusal in the exploitation of their natural resources. The common currency, CFA franc used by 14 of the former colonies is controlled by the French Treasury, that holds a sizeable amount of the countries’ revenue deposits, which they are made to borrow at economic interests.
For instance, Niger is rich in priced minerals such as uranium and gold, but foreign companies, particularly those from France, mine these natural resources to enrich and develop their countries, leaving Niger and its estimated 26 million population in penury and abject poverty.

It is no wonder, that the Niger junta has now demanded renegotiation of the country’s economic and other contracts with France to ensure that the people of Niger maximized the benefits of their God-given resources.
Insecurity, underpinned by terrorism and Islamic insurgency in West Africa and the Sahel, are the reason for the military presence of France, its European and American allies in the region.
But the junta regimes and local populations are unimpressed. They claim that the foreign forces are instead pursuing their own agendas in the name of fighting terrorism.
Meanwhile, the U.S. which has some 1,100 troops in Niger has been conspicuous in its ambivalence over the military takeover in Niger. After initial condemnation and public show of support and pressure on the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) to take tough measures against the Niger junta, Washington has since found some accommodation with the junta.
Curiously, Washington remains undecided whether the 26 July putsch “is a coup” or “an attempted coup,” while America’s newly appointed Ambassador to Niger recently assumed duty in Niamey. Also, following an understanding reached with the junta, the U.S. has resumed its strategic military drone flights from Niger for surveillance operations across Africa.
At the same time, continued pressure by France and America on ECOWAS to act, has led to the regional bloc’s unmet threat to intervene militarily to restore constitutional order in Niger.

ECOWAS now has every reason to feel undermined and boxed into a tight corner by the inconsistent and double-faced positions by Paris and Washington on Niger, apparently driven by fear in the West of being displaced in Africa by Russia and China.
However, there could be some silver linings in the cloud of geopolitical game in Niger, particularly a bitter lesson for African leaders that international relations are about national interests and the fact that it is Africans that should solve African problems.
For African countries to develop and prosper, they must be strategic and necessarily review their relationships with foreign powers. Africa is not zero-poor but only badly run and impoverished, no thanks to the conspiracy and unholy alliance between African rulers and powerful foreign interests, be they France, EU, America, China, Russia, or Turkey.
ECOWAS is renowned for achievements in the domain of peace and security. It has to reset its conflict management and resolution strategies with dynamic and properly nuanced home-grown tools, taking into consideration the peculiarities of each situation.
It is obvious that kinetic option in Niger is not only unpopular but risky with potentially unintended catastrophic consequences. Diplomacy, and backchannel initiatives stand a better chance of success when complemented with effective regional sanctions.
Lastly, after more than 60 years of unmitigated exploitation of Africa’s resources through its compromised and corrupt leaders, under the guise of support, France and its Western allies must now listen to the deafening voices of the long-suffering populations yearning for true freedom as opposed to the flag independence granted the former colonies.(Flowerbudnews)
*Paul Ejime is a Global Affairs Analyst and Consultant on Peace & Security and Governance Communications